In the pursuit of flawless and radiant skin, facial pigmentation stands as a common concern for many individuals. Whether it’s caused by sun damage, hormonal changes, or underlying health conditions, pigmentation issues can have a significant impact on one’s self-esteem and overall appearance.
While various skincare products and treatments promise solutions, the role of diet in managing facial pigmentation is often overlooked. A well-balanced and nutrient-rich diet can play a crucial role in reducing pigmentation and promoting clear, even-toned skin.
Understanding Skin Pigmentation
Facial pigmentation refers to the uneven distribution of melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes. It can manifest as dark spots, patches, or uneven skin tone.
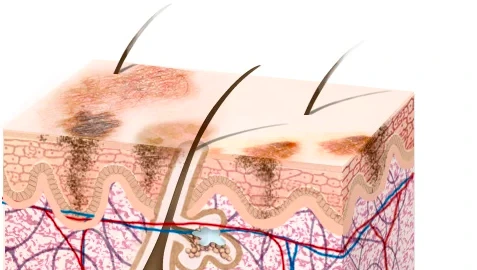
The primary causes of facial pigmentation include:
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged and unprotected exposure to the sun’s harmful UV rays can trigger an overproduction of melanin, resulting in dark spots or freckles.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, often associated with pregnancy, menopause, or certain medical conditions, can lead to increased melanin production and subsequent pigmentation.
- Inflammation and Skin Trauma: Skin inflammation caused by conditions like acne or eczema can stimulate melanin production, leading to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Genetics: Genetic predisposition can influence an individual’s susceptibility to pigmentation issues.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle Habits: Poor lifestyle choices, including a high-sugar diet, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption, can exacerbate pigmentation problems.
Role of Diet in Managing Skin Pigmentation
The adage “you are what you eat” holds true when it comes to skin health. A diet rich in essential nutrients can contribute to improved skin tone and texture. Here are key dietary factors that play a significant role in managing facial pigmentation:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
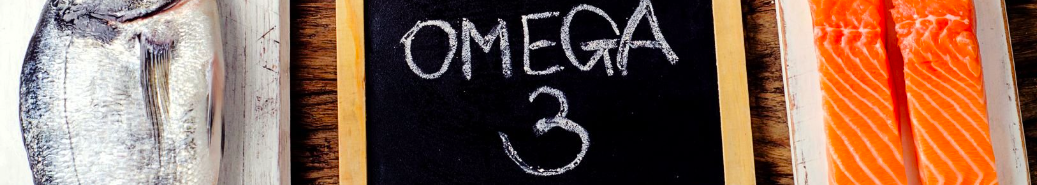
Found in fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, and sardines), flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3 fatty acids possess anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe skin inflammation and reduce pigmentation caused by skin trauma.
Vitamin C for Skin health:
This vitamin is essential for collagen production, which supports skin structure and promotes an even skin tone. Foods like oranges, kiwi, bell peppers, and broccoli are excellent sources of vitamin C.
Skin and Turmeric:
Curcumin, a compound present in turmeric, has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Including turmeric in your diet can help mitigate pigmentation issues caused by inflammation.
Vitamin E:
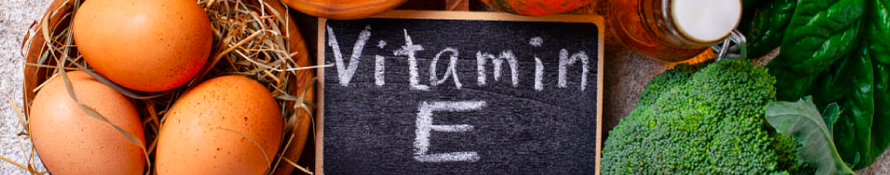
Vitamin E works alongside vitamin C to protect the skin from UV damage and reduce the appearance of pigmentation. Nuts, seeds, and avocados are good sources of vitamin E.
Green Tea:
Green tea is rich in polyphenols that have been shown to have protective effects against UV-induced skin damage. Regular consumption of green tea can contribute to a more even complexion.
Hydrated Skin:

Staying well-hydrated is essential for maintaining skin health. Adequate water intake helps flush out toxins and supports the skin’s natural rejuvenation processes.
Whole Grains:
Opt for whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat, which provide a steady supply of complex carbohydrates. These carbs help regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of insulin spikes that can trigger hormonal imbalances leading to pigmentation.
Collagen-Boosting Foods:

Foods that support collagen production, such as bone broth, lean proteins, and vitamin C-rich fruits, can help improve skin elasticity and reduce pigmentation.
Limit Sugar and Processed Foods:
Diets high in sugar and processed foods can lead to inflammation and exacerbate pigmentation issues. Choose whole, nutrient-dense foods over sugary snacks and fast food.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods:

Antioxidants combat oxidative stress, a major contributor to skin aging and pigmentation. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries (blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries), citrus fruits, spinach, and kale, can help neutralize free radicals and promote healthy skin.
The Bottom Line
In the quest for clear and radiant skin, addressing facial pigmentation requires a holistic approach that includes proper skincare, sun protection, and a nutrient-rich diet. A well-balanced diet incorporates antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and other skin-friendly nutrients. It can significantly contribute to managing pigmentation issues and promoting an even, glowing complexion.
While diet alone may not provide an instant solution, its long-term impact on skin health cannot be underestimated. Embracing a wholesome diet, coupled with effective skincare practices, can lead to the achievement of one’s desired skin goals and renewed confidence.
Read more:
What are some Vitamin B12 Rich Dry Fruits?
Simple Multani Mitti Face Packs for all skin types
पीलिया आहार चार्ट: आपके स्वास्थ्य के लिए मार्गदर्शिका





